Overview of US Property Taxation
I give below a brief outline of the various property taxes: local and city taxes, federal income tax and state income tax, and finally capital gains tax.
Local Tax
Owners of real estate property in the US are subject to local taxes, independently on whether the property generates income or not. These taxes are generally based on the assessed value of the property. They vary widely depending on the state and county, with an observed range between 0.5% and 3% of value.
The tax bills are sent automatically to the registered owner of the property, and online payments options are generally available. Unlike incomes taxes, there is no need to file a specific return.
Note that a 3% tax typical in Texas on a property returning 10% a year brings down the after-tax return to 7%. This would be equivalent to a 30% tax on gross income. This explains in part the large differences in rental yields between states as landlords generally pay less for an asset that comes with a large local tax liability.
Federal Income Tax
Property rental income from a US property is subject to federal taxation. The federal taxes are collected to the Inland Revenue Service (IRS). It should be noted that the IRS conveniently shifted the onus of collection to the taxpayer: he is responsible for determining whether he needs to file a tax return, for computing the tax and for sending payment for the amount due.
Federal Income Tax Basis
Real estate rental is taxed as a business on its net income. The income statement follows tax rules. Federal and state tax are computed from the profits.
- gross income comes from rents and any other receipts (coin operated laundry, etc.)
- operating expenses corresponds to insurance, fees, repairs, management fees, home office costs
- interest from mortgage and credit card are also deductible
- depreciation from improvements and property that have a life above 12 months are also deductible.
- taxable income is net income = gross income - expenses - interest and depreciation
If spending is categorized as an operational expense, it is fully deductible from income for that year, if it is categorized as a capital expenditure (e.g. if it is an improvement rather than a repair) it needs to be depreciated, which means that the deduction will occur over the life of the expenditure. There are many IRS rules dealing with deductions and expense categorization and amortization. Depreciation is subject to recapture for capital gain when the asset is sold, whether expenses are not.
The deductions allowed are substantial compared to the property gross yield: the deduction for interest expense and for building depreciation at a rate of 3.5% can reduce the gross yield by more than 7%. The management fees, repair, and other costs are all deductible.
Federal Income Tax Rate
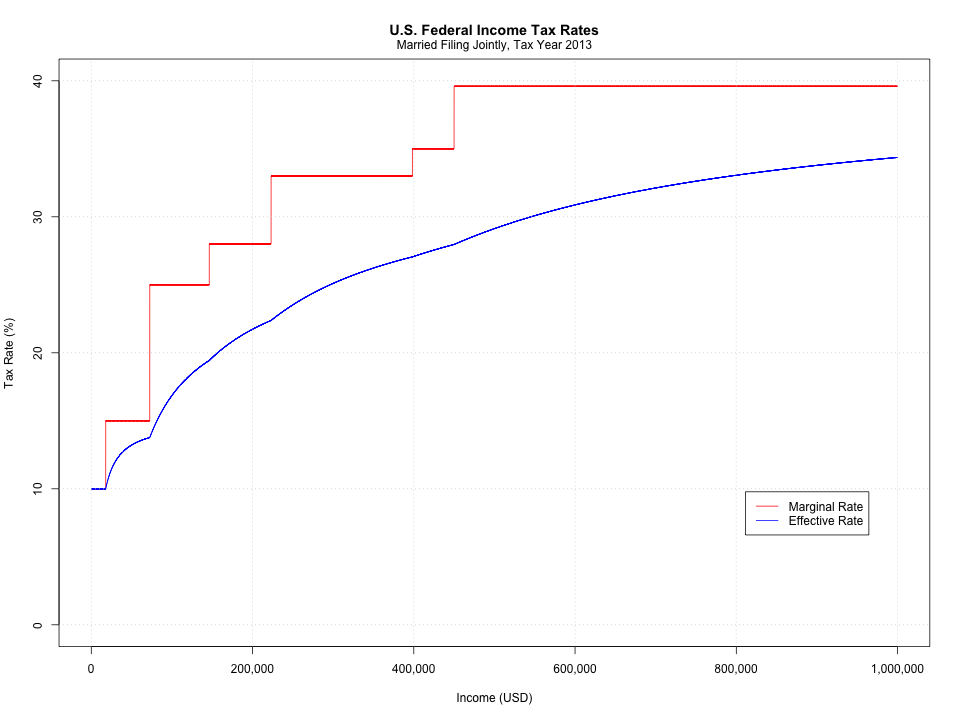
The property net income is then taxed at the taxpayer marginal rate, which goes typically from 0% for revenue below $4000 per year to 39% for revenues above $400,000 per year. The marginal and effective federal tax rate are shown here. The effective and marginal federal income tax rates look as follow:
State Income Tax
State income tax computation requires that your federal income tax be first computed.
Rental property income gives rise to a state tax liability where the property is located requires. Nine states impose no state income tax, in this case, only local tax and federal taxes are due and no state tax return filing is necessary: Alaska, Florida, Nevada, South Dakota, Texas, Washington, Wyoming, Tennessee, New Hampshire. In any other state, you will need to file a state tax return based on the federal return, you can expect a tax rate between 0% and 5%. California and New York being egregious exceptions where state tax income can reach 12%. If you own properties in several states, you will need to determine the income or loss attributable to each state.
Capital Gains Tax
Capital gains tax is due when an investment property is sold at a profit. There are exemptions for houses where the taxpayer has lived continuously. Capital gains are declared on the income tax returns, in a special section as taxation is at a much lower rate.
- short-term capital gain is taxed at a level similar to ordinary income
- long-term capital gains are taxed from 0 to 15% (with a 20% level for 39% marginal bracket taxpayers).
The rationale for the lower level of long-term capital gains tax is to encourage investment.
As a property was subject to a depreciation deduction, the depreciation is going to be taxed by the IRS if the property is sold above the depreciated value. This is called depreciation recapture.
Forms included in a real estate federal tax return
Federal tax filing, in general, is a complicated process. US Residents can use online software or hire an accountant. NRA can not file online, and tax preparation software cannot be bought outside the US. They can either fill the form by themselves or hire an accountant.
To help understand what tax filing looks like in practice, we'll introduce the main tax forms that need to be filled. For our purpose, at least three sets of forms always need to be submitted. These are, in top-down order:
- main income tax form: form 1040 for resident 1040NR for non resident
- real estate net income computation: form 1040 schedule E
- house depreciation computation: form 4562
The state income tax depends on the state where the property is located. They refer to federal tax income forms, so it is necessary to fill federal forms first.
For filing the taxes, the depreciation form needs to be filled first, its result is an input in form 1040 schedule E which needs to be filled second. Form 1040NR is filled last. You can check the links to find explanations.
Additional forms that may apply
- The alternative minimum tax (AMT) is relevant for income that arises from activities that receive a favorable tax treatment. While residential rental activity does not give rise to AMT liability, I am not sure whether some capital gains may give rise to such liability. I would seek advice on this when I sell a property. See form 6251.
- If the net result from real estate operation is negative, the form 8532 needs to be used.
- capital gains declaration in case of sale: form 8949